More than 10 million people worldwide are suffering from Parkinson’s Disease (PD) with around 1 million patients in the US itself. PD is caused by loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain leading to reduced motor function. The available therapies are largely symptomatic and there are no truly disease modifying treatment options available as yet that can protect the loss of dopamine producing neurons. Abl kinases have been shown to be responsible for the deleterious events leading to loss of dopamine neurons in people with Parkinson’s Disease.
(SCC-138) vodobatinib, is a potent, orally active, c-Abl inhibitor with adequate brain penetration that exhibits superior safety/tolerability profile. In preclinical models Vodobatinib has demonstrated protection against the loss of dopamine-producing neurons. This offers vodobatinib the potential to be first-in-class disease-modifying therapy in α-synuclein driven neurodegenerative diseases.
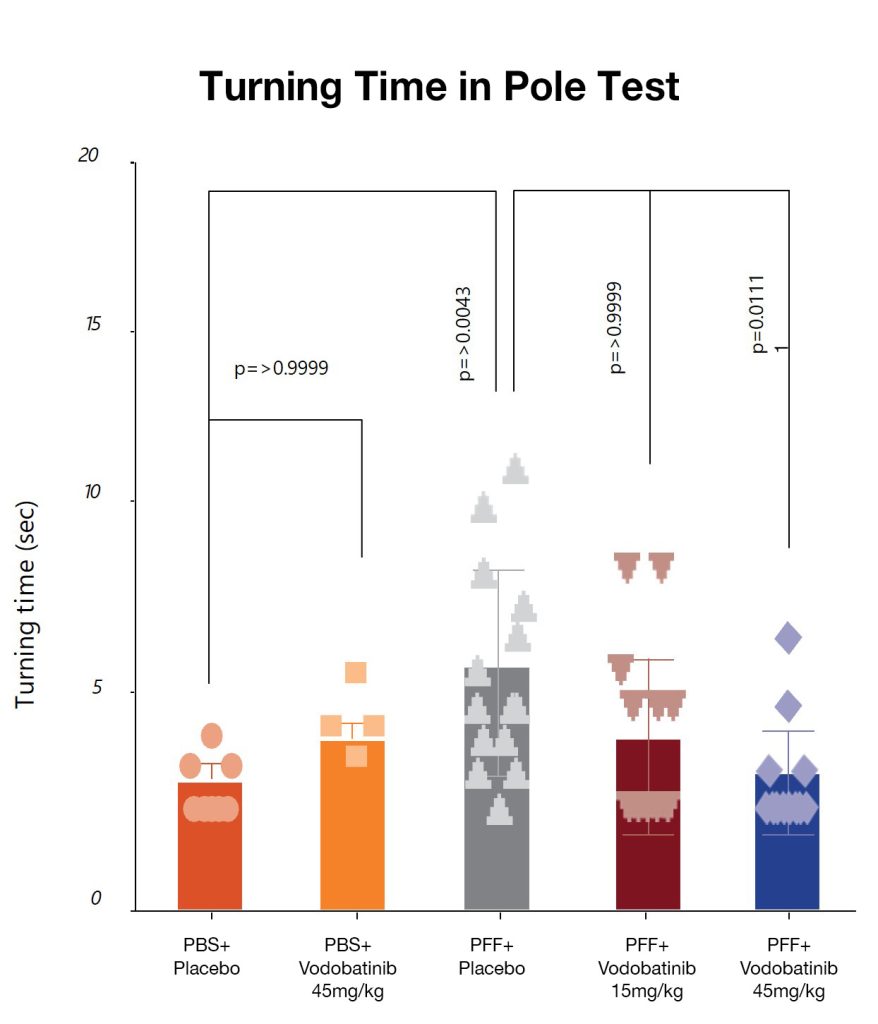
Effects of vodobatinib on behavioral assessments in the PFF-induced mouse model

SPARC has completed two Phase 1 studies with no observed significant adverse events in both studies. The preliminary pharmacokinetic data indicates the presence of drug in the CSF, suggesting that the drug is able to get to its site of intended action.
SPARC has initiated a Phase 2 Study (PROSEEK) to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of (SCC-138) vodobatinib over 500 subjects with early Parkinson’s Disease (PD) across US, Europe and India who are not receiving dopaminergic therapy. Phase 2 readout is expected in 2024.
Publications
- Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of vodobatinib, a neuroprotective c-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders (2023) Ryan R. Walsh, Nitin K. Damle, Sanjay Mandhane, Steven P. Piccoli, Ravi S. Talluri, Damon Love, Siu-Long Yao, Vikram Ramanathan, Orest Hurko
- Vodobatinib, a potent orally bioavailable brain-penetrating inhibitor of c-Abl as a potential neuroprotective agent for treatment of Parkinson Disease (2022) World Congress on Parkinson’s Disease and related disorders P 094; R.R. Walsh. S. Piccoli, R.S.Talluri, S. Mandhane, D. Love, O. Hurko, S.L. Yao, V. Ramanathan, N. Damle
- Results of a phase 1 dose-ranging trial, and Design of a Phase 2 trial, of K0706, a novel C-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for Parkinson’s Disease, Neurology 92 (15 supplement) (2019). P2.8-047. Goldfine, R. Faulkner, V. Sadashivam, O. Omidvar, J.M. Hill, S. Jagadeesan, A. K. Sharma, S.L. Yao